🚀 Unlocking Agile Software Delivery: The Power of Continuous Integration, Continuous Development, Continuous Testing, and Continuous Delivery 🌐
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, organizations are continually seeking ways to accelerate software delivery while maintaining high-quality standards. Enter the world of Continuous Integration, Continuous Development, Continuous Testing, and Continuous Delivery—four interrelated practices that are revolutionizing the software development process. Let's embark on a journey to explore these concepts and understand how they work together to supercharge your software delivery pipeline.
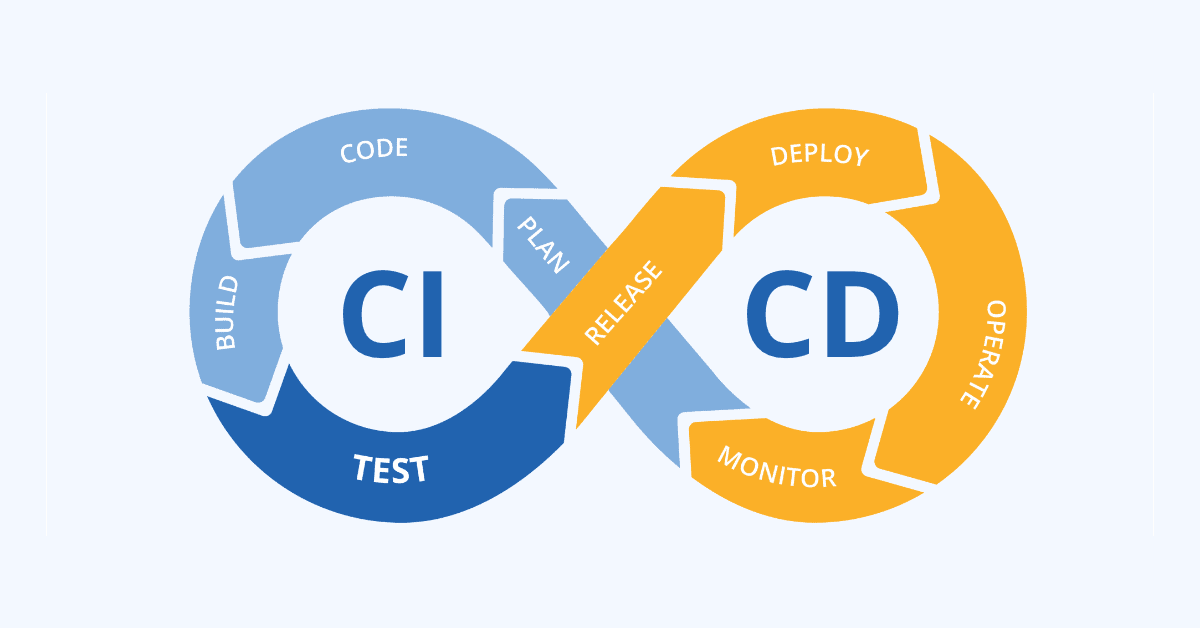
👉 Continuous Integration (CI): Continuous Integration is the heartbeat of Agile development. It involves integrating code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository on an ongoing basis. With each commit, automated build processes and tests are triggered, allowing developers to quickly identify and resolve integration issues. CI promotes early bug detection, collaboration, and a stable codebase.
🎯 Key Benefits of Continuous Integration:
1️⃣ Faster Feedback Loops: By automating build and test processes, CI provides rapid feedback on code changes, enabling developers to catch and address issues early in the development cycle.
2️⃣ Enhanced Collaboration: CI encourages a collaborative environment where developers work together, integrating their changes frequently, reducing conflicts, and fostering teamwork.
3️⃣ Code Quality Assurance: With automated testing in place, CI ensures that the codebase remains stable, preventing the accumulation of technical debt and allowing for faster iterations.
🚀 Continuous Development (CD): Continuous Development complements CI by emphasizing the continuous delivery of new features and enhancements. It leverages iterative development cycles, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to changing market needs. Developers work in short iterations, continuously adding, updating, and refining code. CD fosters agility, innovation, and a rapid feedback loop.
🎯 Key Benefits of Continuous Development:
1️⃣ Agile Responsiveness: CD enables organizations to quickly adapt to market demands, continuously delivering value to customers and gaining a competitive edge.
2️⃣ Innovation Catalyst: With a focus on continuous improvement, CD encourages experimentation and innovation, fueling creativity and pushing boundaries.
3️⃣ Risk Mitigation: Frequent code updates in CD reduce the size and impact of each change, minimizing risks and enabling faster recovery in case of issues.
🔍 Continuous Testing (CT): Continuous Testing ensures that software changes are thoroughly tested throughout the development process. It involves a comprehensive suite of automated tests that validate functionality, performance, security, and user experience. CT facilitates early bug detection, prevents regression, and builds confidence in the software's quality.
🎯 Key Benefits of Continuous Testing:
1️⃣ Early Bug Detection: By running automated tests continuously, CT enables the swift identification of defects, reducing the cost and time required for bug fixing.
2️⃣ Enhanced Test Coverage: CT allows organizations to achieve higher levels of test coverage, ensuring that all critical functionality and use cases are thoroughly validated.
3️⃣ Quality Assurance: With robust automated tests, CT provides assurance that the software meets quality standards, increasing customer satisfaction and trust.
🌟 Continuous Delivery (CD): Continuous Delivery takes the integration of CI, development agility of CD, and comprehensive testing of CT to the next level. It automates the release and deployment process, ensuring that software is always in a releasable state. CD enables organizations to deliver features to production at any time, with confidence and reliability.
🎯 Key Benefits of Continuous Delivery:
1️⃣ Faster Time-to-Market: CD allows organizations to release software updates frequently, delivering value to customers faster and gaining a competitive advantage.
2️⃣ Reliable Releases: With automated deployment pipelines and rigorous testing, CD reduces the risk of human error, resulting in more reliable and consistent releases.
3️⃣ Continuous Improvement: CD fosters a culture of continuous improvement by providing rapid feedback, allowing organizations to learn from user feedback and evolve their software iteratively.
🌐 In conclusion, the synergy of Continuous Integration, Continuous Development, Continuous Testing, and Continuous Delivery empowers organizations to embrace agile software delivery, drive innovation, and exceed customer expectations. By implementing these practices, you can unlock the full potential of your development teams, streamline your software delivery pipeline, and embrace the future of software development.